Senebetennelse i skulderen
Senebetennelse, tendinopati, i skulderen er en irritasjon i en sene, vanligvis som følge av skade eller overbelastning.

Sist oppdatert:
15. okt. 2024
Innhold i artikkelen
Ulike sener i skulderen kan bli betente etter overbelastning. Behandlingen er tilpasning av fysisk aktivitet, øvelser, eventuelt smertestillende og/eller betennelsesdempende medisiner. I noen tilfeller forsøkes kortisonsprøyter eller annen behandling.
Hva er senebetennelse i skulderen?

Senebetennelse, tendinopati, i skulderen er en irritasjon i en sene, vanligvis som følge av skade eller overbelastning. Betennelsen er ikke forårsaket av bakterier eller virus, det er en steril betennelse. Det skilles mellom akutte og kroniske senebetennelser, der de kroniske senebetennelsene betegnes tendinoser. Ved smertetilstander som skyldes overbelastninger, er det vanligvis ingen betennelsesforandringer å finne i senen. Fagfolk mener at betegnelsen senebetennelse da er misvisende, og de bruker gjerne betegnelsene tendinopati og tendinose om disse tilstandene.
De vanligste senebetennelsene i skulderen er lokalisert til følgende sener:


- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Subscapularis
- Biceps
Hovedsymptomer er smerter i skulderen som forverres ved bestemte bevegelser, noe som avhenger av hvilken sene som er betent. Smertene gir redusert funksjon i skulderen. Hos noen opptrer smertene etter uvant arbeid eller aktivitet.
Årsak
Senebetennelser i skuldrene er ganske vanlige lidelser. Supraspinatus tendinopati er den vanligste formen for skuldertendinopati og utgjør 80 prosent av alle tilfeller. Deretter følger infraspinatus. I mindre grad rammes subscapularis og biceps.
Overbelastning er den vanligste årsaken til plagene. Skulderskade er også en vanlig årsak og kan gi etterfølgende senebetennelse. Ved den vanligste typen senebetennelse i skulderen, supraspinatustendinopati, kan plassforholdene under det beinete taket i skulderleddet (akromion) der senen passerer, være dårlige. Dermed oppstår smerte når senen gnisser mot beinet. Dette fenomenet betegnes på fagspråket for "impingement".
Faktorer som disponerer for slik betennelse er:
- Uheldige arbeidsvaner og tungt og ensidig arbeid med mye løfting og bæring, særlig over hodehøyde
- Tidligere skulderskade
Diagnostikk
Sykehistorien vil ofte gi mistanke om diagnosen. Det er viktig å vite hvor smertene sitter, smertegraden, hvilke bevegelser som utløser smertene og om det foreligger risikofaktorer for tilstanden. Ved supraspinatustendinopati er spesielt det å løfte armen ut til siden av kroppen, smertefullt. Ved systematisk undersøkelse av bevegeligheten i skulderen kan legen noen ganger finne ut hvilken sene som er betent.
Typisk for senebetennelse er at smertene forverres ved bruk av senen som er betent. I skulderen kan noen ganger flere sener være betente. Dersom legen er usikker på diagnosen, kan han eller hun sprøyte lokalbedøvelse rundt den aktuelle senen. Hvis smertene forsvinner, bekreftes diagnosen.
Røntgen av skulderen er vanligvis unødvendig, men ved gjentatte betennelser vil det være riktig å foreta en røntgen- eller MR-undersøkelse. I noen tilfeller påvises kalkutfellinger rundt sener.
Behandling
Målet med behandlingen er å dempe smerten samt, redusere betennelsen og øke funksjonen i skulderen. Det er viktig å være klar over at senebetennelser aldri skyldes bakterier eller virus, men er en steril irritasjon eller overbelastning i senen. Konsekvensen av en slik betennelse er økt blodgjennomstrømming i senen, noe som fører til at senen hovner opp, det blir trangt rundt senen, den klemmes mot omgivende strukturer og det oppstår smerter. Noen ganger er det skader som fører til mindre blødninger i senen, og som utløser en slik betennelsesreaksjon. Derfor er antibiotika uten virkning ved senebetennelser. I stedet kan det brukes midler som demper betennelsen, som for eksempel NSAIDs eller eventuelt kortisoninnsprøytninger.
Det er ikke alltid nødvendig å bruke medisiner. I første omgang er det viktig med tilpasning av fysisk aktivitet for å unngå de bevegelsene som utløser eller forverrer smerte. Samtidig bør du unngå å holde armen mest mulig i ro. Da stivner skulderen, og det kan ta lang tid og gi deg mye plager for å få tilbake bevegeligheten.
Det kan være behov for tilrettelegging av arbeid eller eventuelt sykemelding dersom plagene har sammenheng med arbeidssituasjonen din.
Det er viktig at du gjennomfører et program med øvelser for gradvis opptrening.
Treningsøvelser
Din fysioterapeut, manuell terapeut eller lege kan gi veiledning i opptrening som kan føre til bedring av skulderfunksjonen. Du kan også finne videoer nedenfor som demonstrerer hvordan du kan utføre ulike øvelser.
Det finnes et større utvalg av øvelser du kan gjøre. Hva som er "riktig" øvelse for deg, kan være vanskelig å forutsi fordi skulderplagene kan ha oppstått av ulike grunner. Derfor anbefaler vi at du prøver deg frem med de ulike øvelsene for å finne den eller de øvelsene som virker best for deg. Dette gjelder særlig hvis du har opplevd kroniske smerter i andre deler av kroppen tidligere.
Treningen består i øvelser som fremmer god bevegelighet i skulderen og som bidrar til gradvis økende styrke. I starten utføres treningen med ingen eller lette belastninger og mange repetisjoner. Du kan utføre passive tøyninger, men du kan også utføre øvelser der du kombinerer tøyninger av den utstrekte muskulaturen med å spenne/stramme musklene i deler av øvelsen - en kombinasjonsøvelse som betegnes aktive tøyningsøvelser. På sikt kan det også bli aktuelt med styrketrening med vekter.
Ved smertefulle tilstander i muskulaturen vil ofte samvirkende muskler utenfor det området der smerten oppstod, bli spente og stramme og kunne medføre tiltakende og langvarige plager. Derfor anbefales øvelser der også andre tilhørende muskelgrupper inngår i øvelsene - som ved aktive tøyningsøvelser.
På NHI.no finner du videoer som demonstrerer ulike passive og aktive tøyningsøvelser.
Behandlingen bør kombineres med råd om riktige arbeidsstillinger og øvelser for å korrigere nedsatt funksjon og belastningstoleranse.
Her finner du detaljerte instrukser om hvordan du kan trene opp skulderen din ved ulike typer senebetennelse:
Egenøvelser
START-øvelser er kunnskapsbaserte, korte, enkle og trygge treningsprogrammer som pasienter kan gjøre selv uten hjelpemidler. Oppstart gjerne i samråd med fastlegen
Medikamentell behandling
NSAIDs har betennelsesdempende og smertestillende virkninger. Behandlingen brukes først og fremst mot smerte og over kort tid.
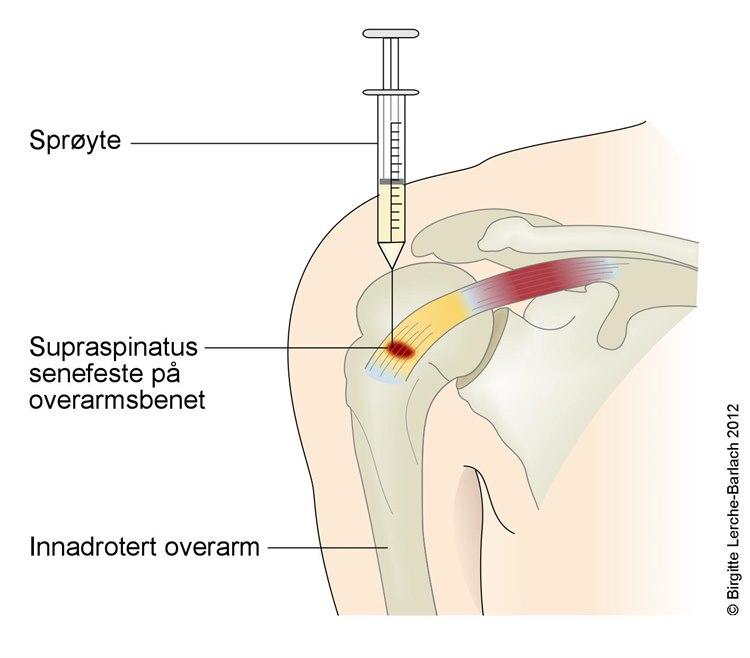
Innsprøytning av kortison (steroider) rundt senefestet, som virker både betennelsesdempende og smertestillende, kan vurderes ved sterke smerter. Sprøyten kan gis i tillegg til behandling med NSAIDs, som alternativ til NSAIDs, eller når smertene har vart i flere uker eller måneder uten bedring.
Ved bare delvis effekt kan injeksjoner gjentas 1-2 ganger med minst 1 ukes mellomrom.
Virkningen av kortisonsprøyter er omdiskutert. Sannsynligvis har de en smertedempende korttidseffekt, men langtidseffekten er ikke bedre enn annen behandling.
Det er ingen klare retningslinjer om hva som er best behandling ved kalkutfellinger rundt sener (peritendinitis calcarea).
Annen behandling
Såkalt trykkbølgebehandling kan være et supplement til øvelsesbehandling. Det anbefales å forsøke dersom man har kalkutfelling i skulderen, men er ikke anbefalt dersom man ikke har kalkutfelling. Trykkbehandling (akupressur) og/eller tverrfriksjonsmassasje er blant de manuelle metodene som fysioterapeuter også benytter.
Kirurgi kan være aktuelt i kroniske tilfeller (tendinoser) for å bedre plassforholdene under beintaket i skulderleddet.
Prognose
Effekten av behandling som beskrevet ovenfor, er vanligvis god ved akutte tilstander. Slik kan smertesirkelen brytes og normal aktivitet etter hvert gjenopptas. Gjentatte eller ikke tilstrekkelig behandlete senebetennelser i skulderen kan føre til langvarige plager. Ubehandlet vil en kronisk senebetennelse kunne vare i årevis med varierende grad av nedsatt funksjon i skulderen.
Vil du vite mer
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Skuldertendinopatier . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Sharma P, Maffulli N. Biology of tendon injury: healing, modeling and remodeling. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2006 Apr-Jun;6(2):181-90. PMID: 16849830. PubMed
- Rees JD, Stride M, Scott A. Tendons--time to revisit inflammation. Br J Sports Med. 2014 Nov;48(21):1553-7. PMID: 23476034. PubMed
- Dean BJ, Gettings P, Dakin SG, Carr AJ. Are inflammatory cells increased in painful human tendinopathy? A systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2016 Feb;50(4):216-20. PMID: 26246419. PubMed
- Kane SF, Olewinski LH, Tamminga KS. Management of Chronic Tendon Injuries. Am Fam Physician. 2019 Aug 1;100(3):147-157. PMID: 31361101. PubMed
- Avdeling for allmennmedisin, Universitetet i Oslo. Trygg på skulder i primærhelsetjenesten. Faglig veileder. Publisert mars 2019. Nettsiden besøkt 16.04.19. www.helsebiblioteket.no
- Ardic, F, Kahraman, Y, Kacar, M, et al. Shoulder impingement syndrome: relationships between clinical, functional, and radiologic findings. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2006; 85: 53. PubMed
- Mayerhoefer ME, Breitenseher MJ, Wurnig C, Roposch A. Shoulder impingement: relationship of clinical symptoms and imaging criteria. Clin J Sport Med 2009; 19: 83. PubMed
- Skjong CC, Meininger AK, Ho SS. Tendinopathy treatment: where is the evidence? Clin Sports Med. 2012;31(2):329–350. PMID: 22341021. PubMed
- Joseph MF, Denegar CR. Treating tendinopathy: perspective on anti-inflammatory intervention and therapeutic exercise. Clin Sports Med. 2015;34(2):363–374. PMID: 25818719. PubMed
- Gaujoux-Viala C, Dougados M, Gossec L. Efficacy and safety of steroid injections for shoulder and elbow tendonitis: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68(12):1843–1849. PMID: 19054817 PubMed
- van der Windt DAWM, Bouter LM. Physiotherapy or corticosteroid injection for shoulder pain? Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62: 385-87. PubMed
- Vandvik PO, Lähdeoja T, Ardem C, et al. Subacromial decompression surgery for adults with shoulder pain: a clinical practice guideline. BMJ 2019; 364: l294. pmid:30728120 PubMed
- Slørdal L, Rygnestad T. Er lokale steroidinjeksjoner effektivt eller ikke?. Tidsskr Nor Lægeforen 2003; 123: 3224-5. PubMed
- Tallia AF, Cardone DA. Diagnostic and therapeutic injection of the shoulder region. Am Fam Physician 2003; 67: 1271-8. PubMed
- Ekeberg OM, Bautz-Holter E, Tveitå EK, et al. Subacromial ultrasound guided or systemic steroid injection for rotator cuff disease: randomised double blind study. BMJ. 2009 Jan 23;338:a3112. PMID: 19168537. PubMed
- Gaujoux-Viala C, Dougados M, Gossec L. Efficacy and safety of steroid injections for shoulder and elbow tendonitis: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68: 1843-9. PubMed
- Hollingworth GR, Ellis RM, Hattersley TS. Comparison of injection techniques for shoulder pain: results of a double blind, randomised study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983 Nov 5;287(6402):1339-41. PMID: 6416401. PubMed
- Bloom JE, Rischin A, Johnston RV,et al. Image-guided versus blind glucocorticoid injection for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;(8):CD009147. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009147.pub2. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 26;8:CD009147. PMID: 22895984. PubMed
- Rhon DI, Boyles RB, Cleland JA.One-year outcome of subacromial corticosteroid injection compared with manual physical therapy for the management of the unilateral shoulder impingement syndrome: A pragmatic randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2014; 161:161. PMID: 25089860 PubMed
- Buchbinder R, Green S, Youd JM. Corticosteroid injections for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;2003(1):CD004016. PMID: 12535501. PubMed
- Relis: Valg av glukokortikoid til lokal injeksjon. Forsdahl s, Vorren S. Publisert: 12.12.2022. Nettsiden besøkt 27.04.23. relis.no
- Wu YC, Tsai WC, Tu YK, Yu TY. Comparative effectiveness of nonoperative treatments for chronic calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017 Aug;98(8):1678-1692.e6 . pmid:28400182 PubMed
- Kim YS, Lee HJ, Kim YV, et al. Which method is more effective in treatment of calcific tendinitis in the shoulder? Prospective randomized comparison between ultrasound-guided needling and extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014 Nov;23(11):1640-6. PMID: 25219475. PubMed
- de Witte PB, Selten JW, Navas A, et al. Calcific Tendinitis of the Rotator Cuff: A randomized controlled trial of ultrasound-guided needling and lavage versus subacromial corticosteroids. Am J Sports Med. 2013 May 21. pmid:23696211 PubMed
- de Witte PB, Kolk A, Overes F, et al. Rotator Cuff Calcific Tendinitis: Ultrasound-Guided Needling and Lavage Versus Subacromial Corticosteroids: Five-Year Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med 2017. pmid:28898104 PubMed
- Coghlan JA, Buchbinder R, Green S, et al. Surgery for rotator cuff disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;2008(1):CD005619. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005619.pub2. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 17;1:CD005619. PMID: 18254085. PubMed
- Lombardi I Jr, Magri AG, Fleury AM. et al. Progressive resistance training in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 59: 615-22. PubMed
- Coghlan JA, Buchbinder R, Green S, et al. Surgery for rotator cuff disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;2008(1):CD005619. PMID: 18254085. PubMed
- Elvsaas IKØ, Flatby AV, Hamidi V, Espeland AL. Akromionreseksjon ved impingementsyndrom i skulder: forenklet metodevurdering. Versjon 2. Oslo: Folkehelseinstuttet, 2021. nyemetoder.no
- Beard DJ, Rees JL, Cook JA, et al. Arthroscopic subacromial decompression for subacromial shoulder pain (CSAW): a multicentre, pragmatic, parallel group, placebo-controlled, three-group, randomised surgical trial. Lancet. 2018 Jan 27;391(10118):329-338. PMID: 29169668. PubMed
- Bang MD, Deyle GD. Comparison of supervised exercise with and without manual physical therapy for patients with shoulder impingement syndrome. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2000; 30: 126-37. PubMed
- Senbursa G, Baltaci G, Atay A. Comparison of conservative treatment with and without manual physical therapy for patients with shoulder impingement syndrome: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2007; 15: 915-21. PubMed
- Cyriax J. Textbook of Orthopaedic Medicine, 7th edn. London: Bailliere Tindall, 1981: 190-239.
- De Winter AF, Jans MP, Scholten RJ, Deville W, van Schaardenburg D, Bouter LM. Diagnostic classification of shoulder disorders: interobserver agreement and determinants of disagreement. Ann Rheum Dis 1999; 58: 272-77. PubMed
- Liesdeck C, van der Windt DAWM, Koes BW, Bouter LM. Soft-tissue disorders of the shoulder: a study of inter-observer agreement between general practitioners and physiotherapists and an overview of physiotherapeutic treatment. Physiotherapy 1997; 83: 12-17. PubMed
- Ioppolo F, Tattoli M, Di Sante L, et al. Clinical improvement and resorption of calcifications in calcific tendinitis of the shoulder after shock wave therapy at 6 months follow-up. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Mar 13. PMID: 23499780. PubMed
- Bannuru RR, Flavin NE, Vaysbrot E, et al. High-energy extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for treating chronic calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2014 Apr 15;160(8):542-9. PubMed