Kronisk mellomørebetennelse
Ved kronisk mellomørebetennelse har man hull i trommehinnen, ofte konstant renning fra øret og smerter i perioder. Tilstanden oppstår oftere hos dem som har hatt mange mellomørebetennelser som barn.

Sist oppdatert:
25. feb. 2022
Innhold i artikkelen
Hva er kronisk mellomørebetennelse?
Trommehinnen skiller mellomøret fra øregangen og det ytre øret. Ved kronisk mellomørebetennelse har man hull i trommehinnen og slimhinnen i mellomøret er kronisk betent. Som regel har man også konstant renning av væske fra øret, mens smerter kan komme i perioder. Det er vanlig å høre dårligere på det syke øret enn på det friske.



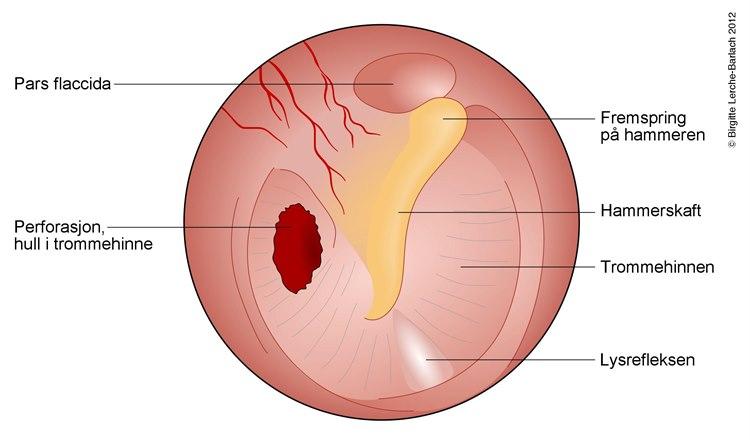
Kronisk mellomørebetennelse forekommer oftere hos personer som har hatt mange tilfeller av akutt mellomørebetennelse som barn, eller som har vært mye plaget med væskedannelse i ørene. Tilstanden er sjelden i den vestlige verden. En fjerdedel av tilfellene oppstår hos barn under fem år, men ellers forekommer tilstanden blant eldre barn og voksne.
Animasjon av mellomørebetennelse
Årsak
Gjentatte akutte mellomørebetennelser kan gi et varig hull, en perforasjon, i trommehinnen. Et slikt hull kan også oppstå som følge av en skade. Dersom man har væske i mellomøret over lengre tid, kan trommehinnen skades og medføre kronisk betennelse og perforasjon.

Når det blir hull i trommehinnen, mister man en viktig barriere mot bakterieangrep. Bakterier kan spres direkte fra huden i øregangen og inn i mellomøret. Ved langvarig betennelse vil også slimhinnen i mellomøret bli skadet, og motstandskraften lokalt i øret blir svekket. Betennelsen fører også i mange tilfeller til at ørebenskjeden ødelegges, og det bidrar til hørselstapet.
Beliggenheten av perforasjonen i trommehinnen er viktig. Et hull sentralt i trommehinnen er ofte mindre alvorlig enn om perforasjonen ligger ute mot kanten. Forklaringen er at en perifer perforasjon disponerer for innvekst av fremmed vev fra øregangen, inn i mellomøret og inn i beinvevet. Det kalles et kolesteatom. Betennelse fører til økt slimproduksjon i mellomøret, og dermed vil det renne slim og puss fra øret.
Kolesteatom
Et kolesteatom er en svulst/kul som vokser fra kanten av trommehinnen og inn i mellomøret. Svulsten er i seg selv ikke ondartet eller farlig, men den trykker på og fortrenger andre strukturer i øret. Dette kan føre til at ørebenskjeden ødelegges, og den kan også skade det omkringliggende beinvevet. Kolesteatomet er som regel en følge av en kronisk betennelse, og fører til forverring av betennelsen. Når det først er dannet et kolesteatom, er det nesten alltid nødvendig med kirurgi for å fjerne dette, og for å stanse den kroniske betennelsen i øret.
Diagnosen
Diagnosen stilles på bakgrunn av den typiske sykehistorien med gjentatte ørebetennelser, stadig renning fra øret og nedsatt hørsel. Ved undersøkelse kan legen se hullet i trommehinnen og pussdannelse i mellomøret direkte. Ofte må legen skylle øregangen forsiktig eller suge ut slim for å få oversikt over trommehinnen.
Behandling
Det er viktig at du unngår å få bakterier inn i mellomøret. Pasienter med hull i trommehinnen må derfor være spesielt oppmerksomme ved bading. Dersom du skal dukke hodet under vann, bør du bruke vanntette ørepropper - dette får du kjøpt på apotek.
Med hull i trommehinnen er du utsatt for plutselige forverringer av infeksjonen i mellomøret. Dette kan arte seg i form av økende smerter eller økende renning av væske/puss fra øret. Slike episoder behandles oftest hos spesialist i øre-nese-hals sykdommer. Behandlingen består av skyllinger og rensing av øret. Det kan også være aktuelt å behandle med antibiotika. Effektiv lokalbehandling med regelmessige skyllinger er avgjørende for å rense opp i mellomøret og få øret til å "tørke opp".
I mange tilfeller utføres operasjon for å tette hullet i trommehinnen. Når trommehinnen blir tett, gjenopprettes funksjonen og svekket hørsel kan normaliseres. Under operasjonen renses øret. Hvis ørebenskjeden i mellomøret er skadet, kan det være mulig å reparere denne skaden slik at hørselen bedres. Eventuelle kolesteatomer må fjernes.
Hos mange pasienter med kronisk ørebetennelse er forandringer i ørene så store at normal hørsel ikke kan forventes selv etter operasjon.
Prognose
Mest alvorlig prognose har de perifere perforasjonene med mulig utvikling av kolesteatom. Prognosen er avhengig av om man får stanset nedbrytingen av benstrukturer tidlig, før alvorlige komplikasjoner oppstår.
Både sentral og perifer perforasjon medfører hørselstap, men en perifer perforasjon kan føre til et alvorligere hørselstap enn en sentral perforasjon. I utviklingsland er kronisk mellomørebetennelse med hørselstap en sterkt medvirkende faktor til lærevansker og dårlige skoleresultater.
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Mellomørebetennelse, kronisk . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Levi J, O'Reilly RC. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM): Clinical features and diagnosis. UpToDate, last updated Jan 06, 2022. UpToDate
- Norsk forening for otorhinolaryngologi, hode- og halskirurgi. Kronisk otitt hos barn og voksne. Veileder for øre-nese-halsfaget. 2011, www.legeforeningen.no
- Seibert JW, Danner CJ. Eustachian tube function and the middle ear. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2006; 39: 1221. PubMed
- Oktay MF, Cureoglu S, Schachern PA, Paparella MM, Kariya S, Fukushima H. Tympanic membrane changes in central tympanic membrane perforations. Am J Otolaryngol 2005; 26: 393. PubMed
- Ricciardiello F, Cavaliere M, Mesolella M, Iengo M. Notes on the microbiology of cholesteatoma: clinical findings and treatment. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 2009; 29: 197. PubMed
- Lasisi AO, Olayemi O, Irabor AE. Early onset otitis media: risk factors and effects on the outcome of chronic suppurative otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2008; 265:765. PubMed
- Bhutta MF, Williamson IG, Sudhoff HH. Cholesteatoma. BMJ 2011; 342: d1088. PubMed
- Maharjan M, Kafle P, Bista M, Shrestha S, Toran KC. Observation of hearing loss in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media tubotympanic type. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ) 2009; 7: 397. PubMed
- Lemmerling MM, de Foer B, VandeVyver V, et al. Imaging of the opacified middle ear. Eur J Radiol 2008; 66: 363-71. PubMed
- Levi J, O'Reilly RC. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM): Treatment, complications, and prevention. UpToDate, last updated Jan 06, 2022. UpToDate
- Macfadyen CA, Acuin JM, Gamble CL. Topical antibiotics without steroids for chronically discharging ears with underlying eardrum perforations. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD004618. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004618.pub2. The Cochrane Library
- Macfadyen CA, Acuin JM, Gamble CL. Systemic antibiotics versus topical treatments for chronically discharging ears with underlying eardrum perforations. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD005608. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005608. DOI
- Omran A, De Denato G, Piccirillo E, Leone O, Sanna M. Petrous bone cholesteatoma: management and outcomes. Laryngoscope 2006; 116: 619. PubMed
- Roth JA, Pandit SR, Soma M, Kertesz TR. Ossicular chain reconstruction with a titanium prosthesis. J Laryngol Otol 2009; 123: 1082. PubMed
- Leach AJ, Morris PS. Antibiotics for the prevention of acute and chronic suppurative otitis media in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 4. Art. No.: CD004401. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004401.pub2. DOI
- Wallis S, Atkinson H, Coatesworth AP. Chronic otitis media. Postgrad Med. 2015 May;127(4):391-5. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2015.1027133 DOI