Borreliose etter flåttbitt
Ved omtrent 98 prosent av alle flåttbitt skjer det ingen overføring av smitte, og du blir ikke syk. Cirka to av 100 flåttbitt fører til sykdommen som kalles borelliose.

Sist oppdatert:
8. aug. 2024
Hva er borreliose?
Borreliose er en sykdom som skyldes infeksjon med bakterien Borrelia burgdorferi, som overføres til mennesker ved flåttbitt. Sykdommen kalles også Lymes sykdom.
De aller fleste flåttbitt fører ikke til sykdom. Det er store lokale variasjoner når det gjelder andelen av flått som inneholder smitte. Det er funnet smitte i alt fra 1-2 prosent til over 60 prosent av flått i ulike studier. I gjennomsnitt oppstår sykdom kun etter ca 2 prosent av alle flåttbitt i Norge, det vil si at 98 av 100 flåttbitt ikke fører til sykdom.
Det har vært en økning i antall meldte tilfeller av borreliose i Norge de siste årene. I 2021 ble det meldt 536 tilfeller mot 510 i 2020 og 488 i 2019. Flest tilfeller rapporteres fra Vestland (119) og Agder (99).
Risikoen for smitteoverføring ved bitt av flått er liten selv i de mest utsatte områdene, og ikke alle som blir smittet, får symptomer. En stor del av befolkningen i endemiske områder har vært smittet med Borrelia og har antistoffer (10-20 prosent).
Animasjon av borreliose
Blant dem som utvikler sykdom, er det vanlig å beskrive tilstanden i tre ulike stadier eller ytringsformer:
Stadium 1 - tidlig lokalisert infeksjon
Fra 2-30 dager etter et flåttbitt (som ikke alltid har blitt oppdaget!) ses et typisk, ringformet, svakt rødt utslett som brer seg utover fra bittstedet. Dette kalles erytema migrans - et vandrende rødt utslett. Utslettet blir vanligvis større enn 5 cm i diameter, ofte omkring 15 cm, men kan også bli mye større. Det er vanlig at utslettet etter hvert får en avblekning i sentrum. De fleste (60-80 prosent) som blir smittet, får dette utslettet, men du kan være smittet selv om du ikke har hatt utslett. Samtidig med utslettet får du vanligvis litt sykdomsfølelse, men oftest forløper det hele uten feber. Dette første stadiet varer vanligvis 2-4 uker, og utslettet glir gradvis over av seg selv, også uten noen form for behandling.

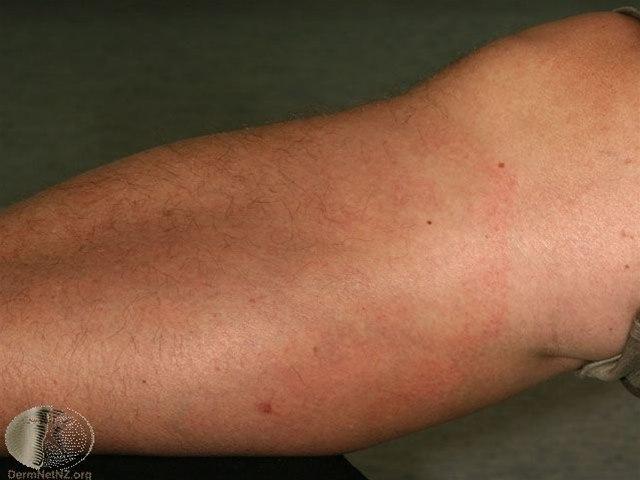







Stadium 2 - tidlig utbredt sykdom
Dersom bakterien i tidlig fase spres med blodet til andre deler av kroppen, kalles det tidlig generell eller tidlig utbredt sykdom. Dette skjer vanligvis 4-8 uker, eventuelt helt opptil 12 uker etter flåttbittet. Mange har da hatt erytema migrans på forhånd. I denne fasen er det først og fremst spredning av bakterien til hjerne og nerver, eller til muskler og ledd som gir plager. Bakterien kan føre til en mild form for hjernehinnebetennelse med plagsom hodepine. Nerverøtter kan også bli angrepet og føre til smerter i nakke, skuldre, lår eller armer. Man kan også få betennelse i nerver og lammelser i enkelte nerver - ansiktslammelse er vanligst. Ved spredning til ledd er leddsmerter vanlig, og noen kan få hevelser i ledd. Ved tidlig spredning av bakterien kan også hjertet bli påvirket. Hos noen ser man mange ringforma utslett selv om man kun har fått ett enkelt flåttbitt. Også dette andre stadiet vil hos de fleste gli over av selv uten behandling.
Stadium 3 - sen utbredt sykdom
Stadium tre kan opptre måneder til år etter smitten hos personer som ikke har fått behandling med antibiotikum i stadium 1 eller stadium 2. Dette stadiet kan vise seg ved et utslett på oversiden av armer eller ben - det ses en blå/rød misfarging og huden blir arraktig og tynn. Sykdommen kan også vise seg ved kroniske leddsmerter eller ved hodepine, konsentrasjonsvansker, eventuelt lammelser og svekket følsomhet i områder av huden.
Post Lyme syndrom
Noen pasienter har plager med kroniske smerter, leddplager, hodepine og konsentrasjonsvansker i lang tid (mange år) etter borrelia-infeksjon. Dette gjelder også pasienter som har fått riktig antibiotikabehandling i tidlig stadium av sykdommen. Det er en del usikkerhet og uenighet både blant eksperter og pasienter om dette skyldes at infeksjonen blomstrer opp, eller om det er plager som skyldes skader etter tidligere infeksjon. Ekspertenes teori er at dette i de fleste tilfeller er forårsaket av skader på nerver eller ledd, og ikke et uttrykk for at bakterien fortsatt er til stede.
Årsak
Bakterien, en spiroket, finnes først og fremst hos mus, rådyr, harer og noen fuglearter. Flåtten (Ixodes ricinus) får bakterien i seg ved å suge blod fra et dyr som har bakterien i kroppen. Flåtten trives best i områder med fuktig skogbunn og vekslende løvskog og åpen mark, og den finnes i kyststrøk fra Hvaler til Helgeland. Når flåtten biter mennesker, og spesielt hvis den får sitte fast og suge blod en tid (over 12-24 timer), kan den overføre bakterien til mennesker. De fleste flått har ikke smitten i seg, og en antar at bare ca. 2 prosent av alle flåttbitt fører til sykdom.
Flåtten har tre utviklingsstadier: larve, nymfe og voksen og varier i størrelse fra 1 til over 10 mm, avhengig av stadium og hvor mye blod den har sugd. Særlig nymfene går på mennesker, og av disse kan opptil 30 prosent være infisert med spiroketen.
Risikofaktorer
- Opphold i risikoområder uten tilstrekkelig beskyttelse. Det er viktig at man dekker kroppen med klær (bukser, lange ermer, sokker) ved opphold i risikoområder.
- Bitt av flått der flåtten får sitte lenge og suge blod.
- Dersom man får flåttbitt, anbefales det å fjerne denne så snart som mulig. Dette gjøres ved å dra flåtten rett ut f.eks. med pinsett eller med fingrene. Den lille resten som sitter igjen, gjør ingen skade og bør få være i fred.
Diagnosen
Utvikling av en større rød sone (erytema migrans) rundt et flåttbitt, oftest ca. 2 uker etter bittet, er typisk for sykdommen. Dersom det i tillegg kommer allmennsymptomer som beskrevet, er dette en sikker diagnose. Mange flåttstikk kan gi en liten rød sone på 1-2 cm rundt stikkstedet, på samme måte som andre insektstikk. Dette er ufarlig og betyr ikke at man er smittet.
Stadium 1
Typisk er at et rødt utslett plutselig oppstår etter flåttbitt. Utslettet sprer seg ringformet, og det er ingen eller bare ubetydelig skjelling eller kløe. Det kan forekomme lett feber og lokal hevelse av lymfeknuter. Utslettet og sykdommen går tilbake av seg selv i løpet av 2 til 4 uker, men dette kan variere mye.
Stadium 2 og 3
Spredning via blod eller lymfe kan gi en lang rekke symptomer dager til uker etter bakterieoverføringen. Det vanligste er hudforandringer, skader i nervesystemet (lammelser, tap av følesans) og leddbetennelser (verk og hevelse i leddene).
Prøver
I stadium 1 har man ingen nytte av blodprøver eller andre prøver. Diagnosen stilles ut fra det typiske utslettet.
I sykdommens andre stadium utvikles langsomt antistoffer i kroppen. Antistoffer dannes av kroppens immunforsvar. Tidlig i andre stadium kan antistoffer mangle, men i løpet av 3-4 uker vil de fleste ha dannet antistoffer, og etter 8 uker finner man antistoffer hos så godt som alle.
De testene som brukes i norske laboratorier, er de aller mest avanserte og mest pålitelige som finnes. Men prøvene kan gi feil utslag tidlig i forløpet, enten ved at antistoffer ikke har rukket å bli dannet, eller at antistoffer fra infeksjoner mange år tilbake fortsatt kan være tilstede, og gi falskt positive svar.
Ved mistanke om alvorlig borreliainfeksjon hvor første prøve er negativ, kan det være aktuelt å ta en ny blodprøve etter 4-6 uker, og det kan være aktuelt å undersøke mer enn en test.
Ved mistanke om at det foreligger betennelse i hjernehinner eller hjernevev, må man innlegges i sykehus der det blant annet gjøres spinalpunksjon - dvs. at en tar en prøve fra ryggmargsvæsken.
Behandling
Formålet med behandlingen er å bli kvitt infeksjonen og å forebygge komplikasjoner. Borreliabakterien er følsom for en rekke typer antibiotika. Som oftest gis vanlig penicillin i tablettform. Dersom man får behandling i det første stadiet (kun erytema migrans), vil en 10-dagers kur føre til helbredelse i de fleste tilfeller.
Dersom sykdommen tidlig spres til andre deler av kroppen, brukes litt mer bredspektret antibiotikum, og kuren strekkes til 3 uker. Også denne behandlingen fører til helbredelse, men noen kan ha plager i lengre tid etter behandlingen.
I unntakstilfeller dukker sykdommen først opp lang tid (måneder til år) etter flåttbittet. Dersom det foreligger lammelser eller betydelig grad av smerter, kan man se at plagene kan vedvare også etter gjennomført behandling. Men selv i dette sene stadiet ser det ut til at 3 ukers behandling med antibiotika direkte i blodet er tilstrekkelig til å knekke infeksjonen. Men plagene kan vedvare lenge etter at infeksjonen er behandlet.
Forebyggende behandling
Det finnes ingen tilgjengelige vaksiner mot borreliose i Norge. Vaksinen som omtales som "flåttvaksinen", beskytter mot hjernebetennelse forårsaket av et virus (TBE-virus) som smitter gjennom flåttbitt og ikke mot borreliose.
Les mer om skogflåttencephalitt.
Ved ferdsel i terreng i utsatte områder ved kysten bør man være dekket med klær slik at flått ikke så lett fester seg (se forebygging av flåttbitt). Insektmidler kan benyttes og synes å redusere risiko for at flåtten slår seg ned.
Inspeksjon av huden og rask fjernelse av fastsittende flått anbefales. Risiko for borreliasmitte øker vesentlig ved kontakttid over 12-24 timer. Flåttkroppen kan fjernes med fingrene eller pinsett, ved å ta tak og trekke flåtten rett ut (se video ). Kjemiske stoffer, fett eller lignende frarådes, fordi de forsinker fjernelsen. Det er ikke farlig om en del av bittredskapen skulle sitte igjen i huden. Den vil avstøtes som et hvilket som helst overflatisk fremmedlegeme.
Bakteriehemmende sårsalve (reseptbelagt medisin) på bittstedet etter flått kan muligens redusere risiko for borreliasmitte. Såret kan med fordel vaskes med såpe og rennende vann.
Det anbefales ikke å bruke antibiotika ved ethvert flåttstikk, fordi bare ca. 2 prosent utvikler sykdom (erythema migrans). Anbefalt tiltak er å observere bittstedet de følgende 14 dager og gi behandling dersom erythema migrans utvikler seg.
Prognose
Sykdommen starter med milde influensaliknende symptomer og rødt utslett, og stanser opp der etter behandling. Også uten behandling vil mange bli friske etter første stadium. I stadium 2, fire til tolv uker etter flåttbitt, kan det komme forandringer i nervesystemet, eller i muskler og ledd. Også i dette stadiet stanser sykdommen opp ved behandling. I stadium 3, måneder til år senere, kan det forekomme leddbetennelse, hudforandringer eller lammelser og nervesmerter.
Ved riktig behandling er prognosen god! Noen får imidlertid vedvarende plager på tross av adekvat behandling.
Husk at 98 prosent av alle flåttbitt ikke fører til smitte. I disse tilfellene skal man ikke bruke antibiotika.
Personer som har hatt borreliose, kan smittes og få ny infeksjon, men det skjer ganske sjelden, ifølge amerikanske tall hos 1 til 15 prosent.
Vil du vite mer
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Borreliose . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Kullberg BJ, Vrijmoeth HD, van de Schoor F, Hovius JW. Lyme borreliosis: diagnosis and management. BMJ. 2020;369:m1041. Published 2020 May 26. PMID: 32457042 PubMed
- Shapiro ED. Clinical practice. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 2014 May 1;370(18):1724-31. PMID: 24785207 PubMed
- Stanek G, Wormser GP, Gray J. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet 2012; 379: 461. pmid:21903253 PubMed
- Smittevernhåndboka. Lyme borreliose - håndbok for helsepersonell. Folkehelseinstituttet, sist oppdatert 07.09.2022. www.fhi.no
- Eliassen KE, Berild D, Reiso H, Grude N, Christophersen KS, Finckenhagen C, Linbæk M. Incidence and antibiotic treatment of erythema migrans in Norway 2005-2009. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2016. pmid: 27475874 PubMed
- Lyngstad TM, Astrup E, Brandal LT, et al. Årsrapport 2020 - Overvåkning av infeksjonssykdommer som smitter fra mat, vann og dyr, inkludert vektorbårne sykdommer. Oslo: Folkehelseinstituttet, 2021. www.fhi.no
- Årsrapport 2023. Overvåkning av infeksjonssykdommer som smitter fra mat, vann og dyr, inkludert vektorbårne sykdommer. Utgitt av Folkehelseinstituttet, Område for Smittevern, Avdeling for Smittevern og beredskap, Mai 2024 www.fhi.no
- Richter D, Matuschka FR, Spielman A. How ticks get under your skin: insertion mechanics of the feeding apparatus of Ixodes ricinus ticks. Proc Biol Sci 2013; 280: 20131758. pmid:24174106 PubMed
- Cook MJ. Lyme borreliosis: a review of data on transmission time after tick attachment. Int J Gen Med 2015; 8: 1. pmid:25565881 PubMed
- Dunham-Ems SM, Caimano MJ, Pal U. Live imaging reveals a biphasic mode of dissemination of Borrelia burgdorferi within ticks. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 3652. pmid:19920352 PubMed
- Razai MS, Doerholt K, Galiza E, Oakeshott P. Tick bite. 10-minute consultation. BMJ 2020;370:m3029 . PMID: 32816780 PubMed
- Fryland L, Wilhelmsson P, Lindgren PE. Low risk of developing Borrelia burgdorferi infection in the south-east of Sweden after being bitten by a Borrelia burgdorferi-infected tick. Int J Infect Dis 2011; 3: 174. pmid:21168354 PubMed
- Wilhelmsson P, Fryland L, Lindblom P. A prospective study on the incidence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato infection after a tick bite in Sweden and on the Åland Islands, Finland (2008-2009). Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2016; 7: 71. pmid:26341726 PubMed
- Mysterud A, Easterday WR, Qviller L. Spatial and seasonal variation in the prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks in Norway. Parasit Vectors 2013; 6: 187. pmid:3691722 PubMed
- Helsedirektoratet (2021). Nasjonal faglig retningslinje for antibiotika i primærhelsetjenesten nettdokument. Oslo: Helsedirektoratet (sist faglig oppdatert 12. september 2023, lest jan 2025). www.helsedirektoratet.no
- Flåttsenteret. Antistofftester borreliose. Nasjonal kompetansetjeneste for flåttbårne sykdommer. flattsenteret.no
- Flåttsenteret. Nasjonal kompetansetjeneste for flåttbårne sykdommer. Jeg har blitt bitt av flått flattsenteret.no
- Koirala J. Lyme disease. BMJ Best Practice. Last reviewed Dec 2024. bestpractice.bmj.com
- Mygland A, Ljøstad U, Fingerle V. EFNS guidelines on the diagnosis and management of European Lyme neuroborreliosis. Eur J Neurol 2010; 17: 8. pmid:19930447 PubMed
- Ford L, Tufts DM. Lyme Neuroborreliosis: Mechanisms of B. burgdorferi Infection of the Nervous System. Brain Sci. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):789. PMID: 34203671. PubMed
- Pal U, Wang P, Bao F. Borrelia burgdorferi basic membrane proteins A and B participate in the genesis of Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 133. pmid:18166585 PubMed
- Hofman H, Fingerle V, Hunfeld K-P, et al. Cutaneous Lyme borreliosis: Guideline of the German Dermatology Society. Ger Med Sci 2017. pmid:28943834 PubMed
- Høiberg HK, Solheim AM, Noraas S, Lorentzen ÅR. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans ved langvarig borreliainfeksjon. Tidsskr Nor Legeforen 2021; 16: 1541-2. PMID: 34758594 PubMed
- British Infection Association. The epidemiology, prevention, investigation and treatment of Lyme borreliosis in United Kingdom patients: a position statement by the British Infection Association. J Infect 2011; 62: 329. pmid:21421007 PubMed
- Eikeland R, Ljøstad U, Mygland A, Herlofson K, Løhaugen GC. European neuroborreliosis: neuropsychological findings 30 months post-treatment. Eur J Neurol 2012; 3: 480-7. pmid:21999112 PubMed
- Berende A, ter Hofstede HJM, Vos FJ, et al. Randomized Trial of Longer-Term Therapy for Symptoms Attributed to Lyme Disease. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 1209-20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1505425 DOI
- Thortveit ET, Aase A, Petersen LB, Lorentzen ÅR, Mygland Å, Ljøstad U. Human seroprevalence of antibodies to tick-borne microbes in southern Norway. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020 Jul;11(4):101410. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101410. Epub 2020 Mar 8. PMID: 32156478. PubMed
- Harbo SO (leder av arbeidsgruppe). Diagnostikk og behandling av lyme borreliose, Rapport til Helsedirektoratet fra arbeidsgruppen. Oslo: , 2009.
- Bézay N, Wagner L, Kadlecek V, et al. Optimisation of dose level and vaccination schedule for the VLA15 Lyme borreliosis vaccine candidate among healthy adults: two randomised, observer-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, phase 2 studies. Lancet Infect Dis 2024. pmid:38830375 PubMed
- Nadelman RB, Hanincová K, Mukherjee P, et al. Differentiation of reinfection from relapse in recurrent Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 1883-90. New England Journal of Medicine
- Flåttsenteret. Nevroborreliose. flattsenteret.no
- Skogman BH, Glimåker K, Nordwall M, et al. Long-term clinical outcome after Lyme neuroborreliosis in childhood. Pediatrics 2012; 130: 262-9. Pediatrics
- Shadick NA, Phillips CB, Sangha O et al. Musculoskeletal and neurologic outcomes in patients with previously treated Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med 1999; 131: 919-26. PubMed
- Kristiansen BE, Grude N, Tveten Y, Emmert A. Laboratoriediagnostikk ved Lyme-borreliose. Tidsskr Nor Legeforen 2009; 129: 2132-4.
- Lantos PM, Rumbaugh J, Bockenstedt LK, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), American Academy of Neurology (AAN), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR): 2020 Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Jan;73(1):1-9. Epub 2020 Nov 29. PMID: 33251700. PubMed