Primær biliær kolangitt (PBC)
PBC er en autoimmun sykdom av ukjent årsak som særlig rammer kvinner. Tidlig medisinsk behandling bedrer prognosen. Sykdommen ble tidligere kalt primær biliær cirrhose.

Sist oppdatert:
4. jan. 2023
Hva er primær biliær kolangitt?
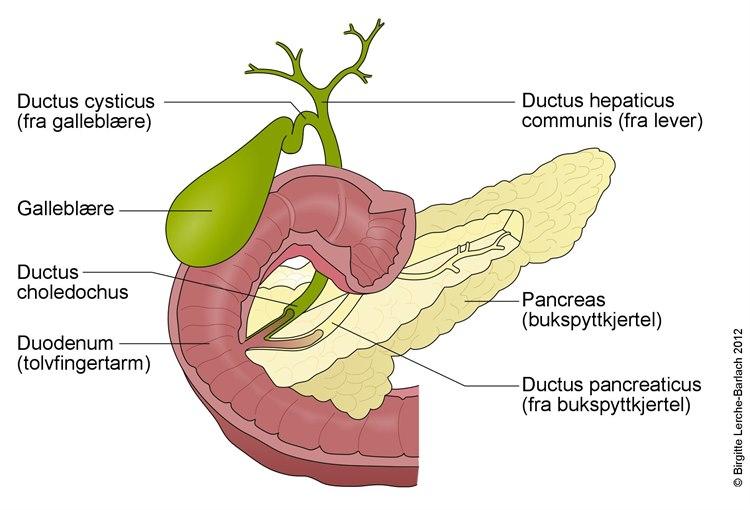
PBC er en autoimmun sykdom hvor immunforsvaret reagerer mot celler i gallegangene i leveren og gir betennelse, arrforandringer og forstyrrelser i leverfunksjonen. Tidlige symptomer er slapphet, plagsom kløe eller tørre slimhinner. Andre symptomer som kommer senere i forløpet kan være fettglinsende avføring, gulsott og blodig oppkast. Symptomer ved langtkommen sykdom er pigmentering og fettknuter i huden.
PBC er en sjelden sykdom. Det finnes ca. 150-400 med sykdommen per million innbyggere. Forekomsten varierer rundt om i verden. Den er høyest i Nord-Europa. Cirka 90 prosent av pasientene er kvinner, hyppigst middelaldrende (40-60 år). Tilstanden er sjelden før 30-års alder. Dersom sykdommen påvises tidlig og medisinsk behandling settes i gang da, kan sykdomsutviklingen bremses.
Årsaker
Årsaken til at immunforsvaret angriper eget vev, er ukjent. Men vi vet at visse arvelige faktorer samt kvinnelig kjønn øker risikoen for utvikling av sykdommen. Miljøfaktorer som for eksempel røyking kan øke risikoen ytterliggere.
Symptomene skyldes sviktende leverfunksjon og at trykket i portvenen (venen inn til leveren) øker. Man får ikke utskilt galle til tarmen på grunn av skadede galleganger. Opphopningen av galle i kroppen gir gulsott, og mangelen på galle i tarmen gir dårligere fettnedbrytning og økte mengder fett i avføringen. Manglende opptak av viktige næringsstoffer blir konsekvensen.
Sent i forløpet av sykdommen kan pasienten oppleve episoder med blodig oppkast. Det skyldes blødning fra utposninger på blodårene i spiserøret, forårsaket av økt blodtrykk i venesystemet inn til leveren. Beinskjørhet kan oppstå på grunn av redusert aktivering av vitamin D i leveren.
Diagnostikk
En eller flere blodprøver på leverfunksjon er del av standardutredningen ved en rekke forskjellige symptomer. Hos personer med vedvarende forhøyede leverprøver der vanlige årsaker til dette er utelukket, bør PBC vurderes som mulig årsak. Den videre utredningen inkluderer spesielle antistoffer. Hos de aller fleste med PBC er antimitokondrie-antistoff forhøyet. Gallepigment (bilirubin) kan være forhøyet.
 Lever og galleblære
Lever og galleblæreUltralyd av lever brukes for å påvise eventuelle andre sykdommer i lever eller galleganger. ERCP kan være en nyttig undersøkelse hvor det føres et lite kikkertrør inn i gallegangene ved hjelp av gastroskop. Kontrastinnsprøytning brukes for å påvise forandringer i gallegangene. Vevsprøve fra leveren foretas med nålestikk gjennom huden. Dette gir sikker diagnose og klargjør hvor langt sykdommen er kommet.
Behandling
Hensikten med behandlingen er å lindre symptomene, bremse sykdomsutviklingen og behandle komplikasjoner. Behandlingen ledes av spesialist i indremedisin. Hovedbehandlingen er medikamentet ursodeoksykolsyre og bør settes i gang så snart diagnosen er stilt.
Ursodeoksykolsyre er en gallesyre med færre leverskadelige egenskaper enn de gallesyrene leveren selv produserer. Den konkurrerer med kroppens egne gallesyrer om opptak i blodet fra nedre del av tynntarmen. Fast behandling med ursodeoksykolsyre vil sørge for at dette vil bli den dominerende gallesyren som kommer over i blodet.
Behandlingen bedrer både symptomer og leveutsiktene, også hos pasienter uten plager. Over uker og måneder vil også leverprøvene bedre seg hos de fleste. Tidligere var levertransplantasjon påkrevd for mange av disse pasientene, men med ursodeoksykolsyre behøver de færreste transplantasjon.
Medisinen tas én gang om dagen. Det kan være aktuelt å øke dosen gradvis over 1-2 uker for å unngå ubehag som kløe og løs avføring. Den største ulempen med behandlingen er dens kostnader og behovet for langtidsbehandling. Smaken av medisinen kan oppleves ubehagelig, og det anbefales å innta den med fruktjuice.
Et nytt preparat, obetikolsyre (Ocaliva), er en syntetisk fremstilt gallesyreanalog. Dette preparater er vist å dempe inflammasjon og symptomer, enten som tillegg til ursodeoksykolsyre eller som eneterapi hos pasienter som ikke tåler ursodeoksykolsyre.
Levertransplantasjon blir nødvendig hos en del av pasientene som utvikler leversvikt. Slapphet og kløe vil vanligvis gå tilbake og den metabolske beinsykdommen vil bli bedre etter forbigående å ha blitt verre de første 6-12 månedene. Noen av pasientene vil få tilbakefall til tross for transplantasjonen.
Prognose
Sykdomsprosessen har ofte vedvart i flere år før pasienten får symptomer og får stilt diagnosen. Hos andre pasienter blir diagnosen stilt før symptomer utvikler seg, som oftes fordi vedvarende forhøyede leverprøver utredes videre. Forløpet varierer mye fra person til person, og er derfor vanskelig å forutsi. Tidlig oppstart av behandling øker leveutsiktene.
Gjennomsnittlig overlevelse etter symptomdebut var tidligere rundt 10 år. Effektiv behandling har redusert behovet for transplantasjon og forbedret overlevelsen. Mange av pasientene der behandlingen startes tidlig, kan ha normale leveutsikter.
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Primær biliær kolangitt . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Jørgensen KK. Primær biliær cholangitt – sjelden sykdom med nytt navn. Gastroenterologen. Publisert 20.10.2017. Siden besøkt 28.10.2019 gastroenterologen.no
- Talwalkar JA, Lindor KD. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Lancet 2003; 362: 53-61. PubMed
- Prince MI, Chetwynd A, Diggle P, Jarner M, Metcalf JV, James OF. The geographical distribution of primary biliary cirrhosis in a well-defined cohort. Hepatology 2001; 34: 1083-88. PubMed
- Lazaridis KN, Talwalkar JA. Clinical epidemiology of primary biliary cirrhosis: incidence, prevalence, and impact of therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 2007; 41: 494-500. PubMed
- Kim WR, Lindor KD, Locke GR III, et al. Epidemiology and natural history of primary biliary cirrhosis in a US community. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1631-6. Gastroenterology
- Kaplan MM, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1261-73. New England Journal of Medicine
- Lindor K. Ursodeoxycholic acid for the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2008; 357: 1524-9. PubMed
- Prieto J, Banales JM, Medina JF. Primary biliary cholangitis: pathogenic mechanisms. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar 1;37(2):91-98. PMID: 33332913 PubMed
- Ueno Y, Moritoki Y, Shimosegawa T, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis: what we know and what we want to know about human PBC and spontaneous PBC mouse models. J Gastroenterol 2007; 42: 189-95. PubMed
- Jones DE. Pathogenesis of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol 2003; 39: 639-48. PubMed
- Howel D, Fischbacher CM, Bhopal RS, Gray J, Metcalf JV, James OF. An exploratory population-based case-control study of primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2000; 31: 1055-60. PubMed
- Jones DEJ, Mackay IR, Snyder N. Primary biliary cirrhosis. BMJ Best Practice, last updated Jan 10, 2017.
- Tanaka A. Current understanding of primary biliary cholangitis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021 Jan;27(1):1-21. Epub 2020 Dec 3. PMID: 33264835 PubMed
- Poupon R. Overview of the management of primary biliary cholangitis. UpToDate, last updated Oct 27, 2021. Siden lest Dec 12, 2022. www.uptodate.com
- Lazaridis KN, Gores GJ, Lindor KD. Ursodeoxycholic acid "mechanisms of action and clinical use in hepatobiliary disorders." J Hepatol 2001; 35: 134-46.
- Paumgartner G, Beuers U. Ursodeoxycholic acid in cholestatic liver disease: mechanisms of action and therapeutic use revisited. Hepatology 2002; 36: 525-31. PubMed
- Rudic JS, Poropat G, Krstic MN et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid for primary biliary cirrhosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Dec 2012, CD000551.pub3. Cochrane (DOI)
- Shi J, Wu C, Lin Y, Chen YX, Zhu L, Xie WF. Long-term effects of mid-dose ursodeoxycholic acid in primary biliary cirrhosis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: 1529-38. PubMed
- Siegel JL, Jorgensen R, Angulo P, Lindor KD. Treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid is associated with weight gain in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2003; 37: 183-5. PubMed
- Nevens F, Andreone P, Mazzella G, et al. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Obeticholic Acid in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. N Engl J Med. 2016; 375: 631-43. PMID: 27532829 PubMed
- Prince MI, Burt AD, Jones DE. Hepatitis and liver dysfunction with rifampicin therapy for pruritus in primary biliary cirrhosis. Gut 2002; 50: 436-39. Gut
- Montano-Loza AJ, Wasilenko S, Bintner J, Mason AL. Cyclosporine A protects against primary biliary cirrhosis recurrence after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2010 Apr;10(4):852-858. Epub 2010 Feb 3. PMID: 20132169 PubMed
- ter Borg PCJ, Schalm SW, Hansen B, van Buuren HR. Prognosis of ursodeoxycholic acid-treated patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: results of a 10-yr cohort study involving 297 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: 2044-50. PubMed
- Poupon R. Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and prognosis of primary biliary cholangitis (primary biliary cirrhosis). UpToDate. Last updated Apr 19, 2022. Site read Dec 20, 2022. www.uptodate.com
- Selmi C, Balkwill DL, Invernizzi P, et al. Patients with primary biliary cirrhosis react against a ubiquitous xenobiotic-metabolizing bacterium. Hepatology 2003; 38: 1250-7. PubMed
- He XS, Ansari AA, Ridgway WM, Coppel RL, Gershwin ME. New insights to the immunopathology and autoimmune responses in primary biliary cirrhosis. Cell Immunol 2006; 239: 1-13. PubMed