Astma hos idrettsutøvere
Både astma og anstrengelsesutløste astmasymptomer rammer eliteidrettsutøvere oftere enn normalbefolkningen. Studier tyder på at utøvernes pustemønster, treningsmengde og treningsmiljø spiller en rolle.

Sist oppdatert:
21. aug. 2025
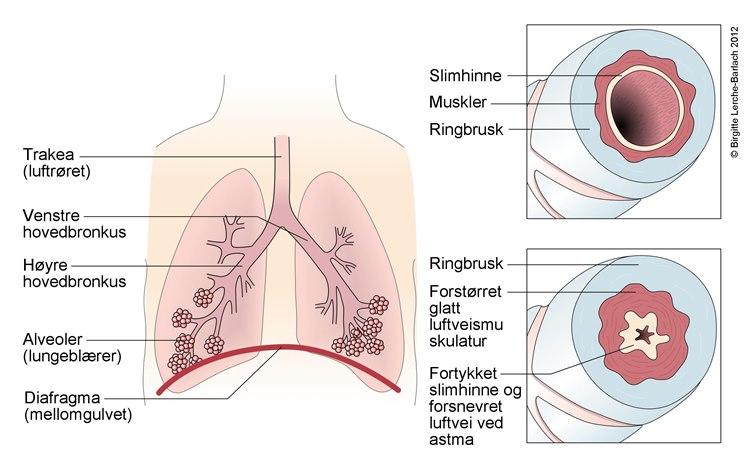
I Norge behandles omtrent én av tjue voksne og én av femten skolebarn mot astma. Forekomsten økte i de fleste europeiske land mellom 1950-2000, men har flatet ut de siste ti årene. I internasjonale studier har man påvist at eliteidrettsutøvere har hyppigere forekomst av astmasymptomer og økt følsomhet i luftveiene enn normalbefolkningen. Årsaken til dette er fortsatt noe uklar, men studiene tyder på en kombinasjon av utøvernes pustemønster, treningsmiljø og treningsmengde som utløsende faktorer. Anstrengelsesutløst bronkospasme, som er astma-liknende anfall utløst av høyintensitets utholdenhetsaktivitet, kan påvises hos cirka en fjerdedel av skøyteløpere, langrennsløpere og svømmere. Denne tilstanden forekommer hyppigere blant personer som har astma, men også personer uten astma kan ha anstrengelsesutløst bronkospasme.
Astmamedisiner var på dopinglisten
Studier har vist at forbruk av medisiner mot astma er høyt hos eliteidrettsutøvere. Flere av astmamedisinene var på World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) sin liste over forbudte stoffer fram til 2011. WADAs dopingregler gjelder over hele verden. I Norge er det Antidoping Norge som håndhever disse reglene.
WADA-regulering av astmamedisiner per juli 2025:
Alle beta-2 agonister er forbudt. Unntak: inhalert salbutamol (korttidsvirkende beta-2 agonist), maks. 1600 mcg pr. døgn, fordelt på flere enkeltdoser, maks. 600 mcg/8 timer. Ved bruk av større doser, annen administrasjonsmåte (f.eks. forstøverapparat), eller ved bruk av annen korttidsvirkende beta-2 agonist (f.eks. terbutalin) må atleten søke om medisinsk fritak (se under). Det finnes også unntak opptil en viss dose for tre langtidsvirkende beta-2 agonister. Ved astma må disse alltid kombineres med et inhalasjonssteroid (ICS).
Den foretrukne behandling av astma og/eller anstrengelsesutløst bronkospasme hos personer fra og med 6-årsalderen, er å bruke en inhalator som inneholder både et inhalasjonssteroid og en beta-2 agonist av type formoterol. Formoterol er en langtidsvirkende, men hurtig innsettende type beta-2 agonist.
Grunnen at man anbefaler kombinasjonen ICS-formoterol og ikke formoterol alene, er at ICS demper betennelse i luftveiene. Behandling av astma med beta-2-agonister alene kan medføre behandlingssvikt og akutte, noen ganger alvorlige astmaanfall. Ved å bruke ICS-formoterol får man både umiddelbar (formoterol) og forebyggende (ICS) effekt.
Avhengig av sykdomsaktivitet brukes kombinasjonsinhalatoren ICS-formoterol fast og ved behov eller kun ved behov. Denne type behandling anbefales iht. aktuelle retningslinjer for astma. Den maksimale døgndose av inhalert formoterol som er tillatt iht. dopinglisten, er 54 mikrogram pr. 24 timer.
Bruk av steroider som tablett, stikkpille, munngel, leppekrem eller per sprøyte, er forbudt. Inhalasjonssteroider som markedsføres i Norge som forebyggende astmabehandling i vanlige doser, er tillatt uten søknad om fritak. Medikamentet montelukast, en forebyggende astmamedisin som har mindre effekt enn ICS, står ikke på WADAs dopingliste.
Ved behov for høyere enn maksimalt anbefalte/tillatte doser, både iht. dopinglisten og Felleskatalogen , må det søkes om medisinsk fritak (se under). Antidoping Norge tilbyr et nyttig legemiddelsøk og mye relevant tilleggsinformasjon på sine nettsider.
Idrettsutøvere som deltar i konkurranser i regi av nasjonale eller internasjonale idrettsorganisasjoner, må i tillegg sette seg inn i regelverket for sitt forbund.
Medisinsk fritak fra dopinglisten
Idrettsutøvere som konkurrerer på nasjonalt eller internasjonalt nivå og som må bruke, administrere eller besitte legemidler som inneholder stoffer eller metoder som er forbudt i henhold til dopinglisten, skal søke om medisinsk fritak (TUE) så raskt som mulig før bruk. Alle andre utøvere over 15 år som vil delta i organisert idrett og som må bruke slike legemidler, kan søke om medisinsk fritak på forhånd. Dersom Antidoping Norge ber om det, skal utøveren søke.
Diagnosen
Korrekt diagnose er viktig, ikke bare i forbindelse med søknad om medisinsk fritak. Det er også viktig for å sikre at utøveren får best mulig behandling. Erfaring fra undersøkelser tyder på at mange idrettsutøvere er underbehandlet og av den grunn forhindres fra å nå toppresultater. Motsatt er det enkelte som får behandling mot astma eller anstrengelsesutløst bronkospasme, uten å ha en slik sykdom. Det er ikke grunn til å tro at slik bruk øker prestasjonsevnen. Det som er avgjørende, er et godt samarbeid mellom idrettsutøveren, behandlingsansvarlig medisinsk personell, treningsansvarlig, idrettsforbundet og eventuelt Antidoping Norge .
Vil du vite mer
Dette dokumentet er basert på det profesjonelle dokumentet Bronkospasme, anstrengelsesutløst . Referanselisten for dette dokumentet vises nedenfor
- Smoliga JM, Mohseni ZS, Berwager JD, et al. Common causes of dyspnoea in athletes: a practical approach for diagnosis and management. Breathe (Sheff) 2016 Jun; 12(2): e22-37. pmid:27408644 PubMed
- Weiler JM, Anderson SD, Randolph C, et al; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Pathogenesis, prevalence, diagnosis, and management of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: a practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010;105(suppl):S1-47
- Smoliga JM, Weiss P, Rundell KW. Exercise induced bronchoconstriction in adults: evidence based diagnosis and management. BMJ 2016; 352: h6951. pmid:26762594 PubMed
- Weiler JM, Brannan JD, Randolph CC, Hallstrand TS, Parsons J, Silvers W, Storms W, Zeiger J, Bernstein DI, Blessing-Moore J, Greenhawt M, Khan D, Lang D, Nicklas RA, Oppenheimer J, Portnoy JM, Schuller DE, Tilles SA, Wallace D. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction update-2016. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Nov;138(5):1292-1295.e36. Epub 2016 Sep 21. PMID: 27665489. PubMed
- Weiss P, Rundell KW. Imitators of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2009; 5(1): 7. pmid:20016690 PubMed
- de Aguiar KB, Anzolin M, Zhang L. Global prevalence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in childhood: A meta-analysis. Pediatr Pulmonol 2018; Jan 24: epub ahead of print. pmid:29364581 PubMed
- Molis MA, Molis WE. Exercise-induced bronchospasm. Sports Health 2010 Jul; 2(4): 311-17. doi:10.1177/1941738110373735 DOI
- Wilber RL, Rundell KW, Szmedra L, Jenkinson DM, Im J, Drake SD. Incidence of exercise-induced bronchospasm in Olympic winter sport athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000; 32: 732-7. PubMed
- Parsons JP, Mastronarde JG. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in athletes. Chest 2005; 128: 3966-74. PubMed
- Weiler JM, Hallstrand TS, Parsons JP, et al. Improving screening and diagnosis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: a call to action. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2014; 2(3): 275-80. pmid:24811017 PubMed
- Parsons JP, Hallstrand TS, Mastronarde JG, et al. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2013. doi:10.1164/rccm.201303-0437ST DOI
- Carlsen KH, Anderson SD, Bjermer L, et al. Exercise-induced asthma, respiratory and allergic disorders in elite athletes: epidemiology, mechanisms and diagnosis: part I of the report from the Joint Task Force of the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (EAACI) in cooperation with GA2LEN. Allergy 2008 Apr; 63(4): 387-403. pmid:18315727 PubMed
- Pasnick SD, Carlos WG 3rd, Arunachalam A, et al. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2014 Dec; 11(10): 1651-2. pmid:25549031 PubMed
- Langhammer A, Jakobsen A, Sjaastad G, Østrem A. Astmaveileder for allmennpraksis. 2022. www.lungeripraksis.no
- Røksund OD, Heimdal JH, Clemm H. Exercise inducible laryngeal obstruction: diagnostics and management. Paediatr Respir Rev 2016 ; Jul 18: S1526-0542. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2016.07.003 DOI
- Røksund O, Clemm H. Exercise indusert laryngeal obstruksjon. Generell veileder i pediatri. Sist faglig oppdatert 01.01.2017. www.helsebiblioteket.no
- Nielsen EW, Hull JH, Backer V. High prevalence of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction in athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2013 Nov; 45(11): 2030-5. pmid:23657163 PubMed
- Krafczyk MA, Asplund CA. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician 2011: 84; 427-34.
- Clemm H, Røksund O. Provokasjonstest for anstrengelsesutløst bronkokonstriksjon. Generell veileder i pediatri. Sist faglig oppdatert 01.01.2017. www.helsebiblioteket.no
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2025. Updated May 2025. Available from www.ginasthma.org ginasthma.org
- Sonna LA, Angel KC, Sharp MA, Knapik JJ, Patton JF, Lilly CM. The prevalence of exercise-induced bronchospasm among US Army recruits and its effects on physical performance. Chest 2001;119:1676-84. PubMed
- Stickland MK, Rowe BH, Spooner CH, et. al. Effect of warm-up exercise on exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012 Mar; 44(3): 383-91. pmid:21811185 PubMed
- Beuther DA, Martin RJ. Efficacy of a heat exchanger mask in cold exercise-induced asthma. Chest 2006; 129: 1188-93. PubMed
- Antidoping Norge www.antidoping.no
- Philip G, Pearlman DS, Villarán C, et al. Single-dose montelukast or salmeterol as protection against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. Chest 2007; 132: 875-83. PubMed
- Leff JA, Busse WW, Pearlman D, Bronsky EA, Kemp J, Hendeles L, et al. Montelukast, a leukotriene-receptor antagonist, for the treatment of mild asthma and exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. N Engl J Med 1998;339:147-52. New England Journal of Medicine
- Edelman JM, Turpin JA, Bronsky EA, et al. Oral montelukast compared with inhaled salmeterol to prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. A randomized, double-blind trial. Exercise Study Group. Ann Intern Med 2000; 132: 97-104. Annals of Internal Medicine
- FDA. Press Announcements. FDA Requires Stronger Warning About Risk of Neuropsychiatric Events Associated with Asthma and Allergy Medication Singulair and Generic Montelukast. March 2020. www.fda.gov